Proportioning of Nominal Mix Concrete
“Each material has its specific characteristics which we must understand if we want to use it. This is no less true of concrete
Contents:
General
Strength of Concrete
Constituents of concrete
Types of concrete
Tests on concrete materials
Nominal Mix Concrete
Proportioning of Nominal Mix Concrete
General:
The concrete mix design is tested for its strength in laboratory. The test specimens used for are cylinders in USA and cubes in India and UK for example and these are used in various countries as per decision taken in these countries.
The concrete mix design in this BLOG shall be discussed on its cube strength basis. (The cube size is kept as 150 mm x 150 mm x 150 mm).
Strength of Concrete
Concrete strength units
Previously, concrete was defined as M 200 or M300. M200 means the 200 kg/centimeter 2.
Now it is defined as M20 or M30. M30 means 20 Newton/mm2.
N = 1/10 Kf (Kilogram force)
As such M 200 Kg/cm2 is same as M 20 N/mm2
Also, 1N/mm2 = I MPa (Mega Pascale)
The concrete strength unit is in MPa (Megapascal) and N/mm2
For example, as 30 MPa (Megapascal) or 30 N/ mm2
Constituents of concrete
The concrete Is composed of following ingredients (in specific limits as per codes and guidelines).
Sand-Natural or Crushed or mix of natural and crushed
Aggregates- Natural or Crushed or mix of natural and crushed
Cementing Materials (Different type of cementing materials are – various types of cements, epoxy resins etcetera required for achieving the desired strength).
Admixtures
Water
The above ingredients are manufacture or collected to the required specifications for concrete production, to maintain the designed concrete strength and workability (Workability means the ease with which concrete can be moved and placed in forms without segregation )
The strength of concrete, produced from these ingredients further depends on production and placement of concrete, along with variations in the properties of constituents of concrete.
Types of Concretes
Regular concrete (ordinary concrete up to M 60
High-strength concrete- Above M 60
Stamp ed concrete-Concrete laid over the main concrete such as architectural concrete
High-performance concrete (have following desirable features)
Ease of placement
Compaction without segregation
Early age strengt
Long-term mechanical properties
Permeability
Density
Heat of hydration
Toughness
Volume stability
Long life in severe environments
Ultra-high-performance concrete
Self-consolidating concretes
Vacuum Concrete
Shotcrete
Limecrete
Pervious concrete
Nailing Concrete
Tests on concrete materials
The various tests suggested for constituents of concrete are as follows: (These may be modified as per work specifications)

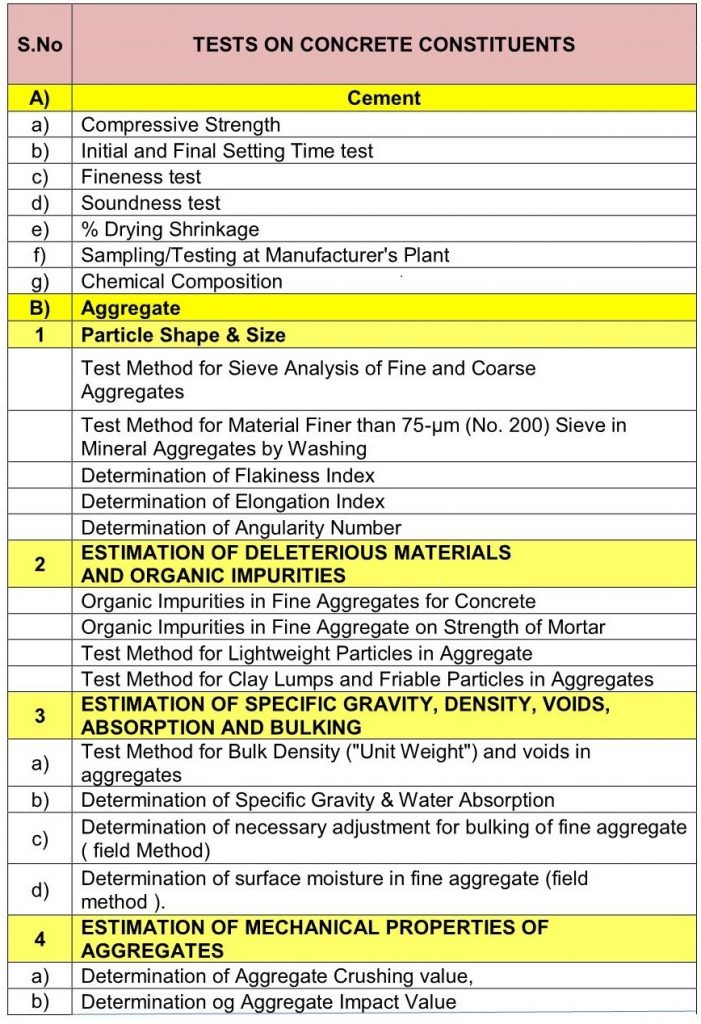
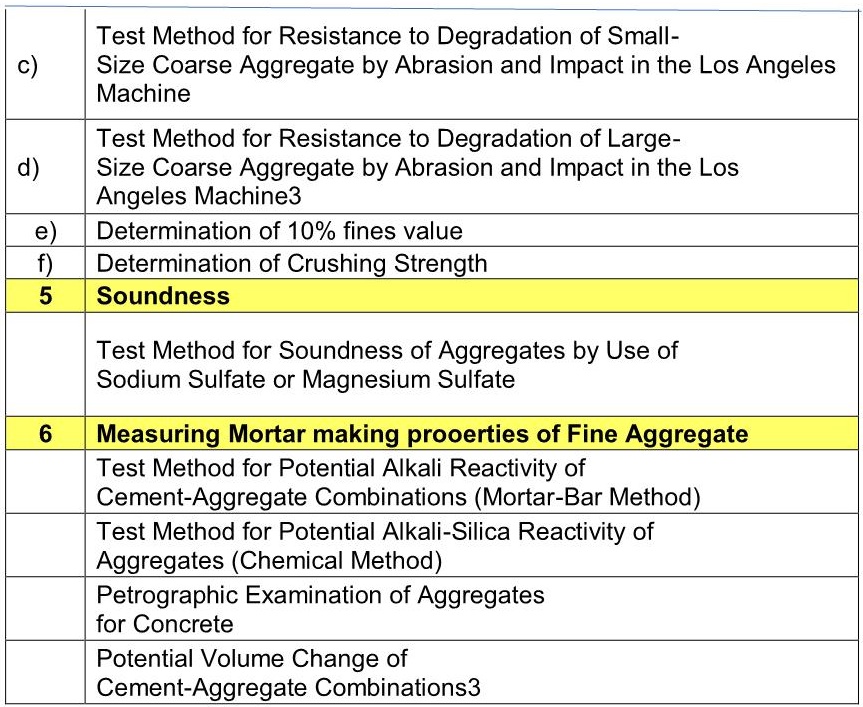
The test results have defined limits of acceptance, adopted on good practices (standards, codes, etcetera)
Variations in quantities of concrete as required are done.
In order to design a mix of desired strength the concrete, the concrete constituents are specifically proportioned on the basis of good experience, practices are available in the form standard and codes.
The results obtained based on mix proportioning are put to further trials and finally the desired mix proportion is used to produce concrete. It is a good practice to carry on mix proportioning at intervals to accommodate any variations in the qualities of constituents of concrete.
Finally, workability durability and strength are the factors that govern mix proportioning.
Nominal Mix Concrete
IS 456 – Plain and Reinforced concrete code of practice, suggest to use Nominal Mix concrete up to M20 and Design Mix concrete above M20
Nominal mix concrete is not designed and it may use excess quantity of cement and must be use for small quantiles of works as per direction and approval of Engineer in Charge.
However, if the quality of M20 grade concrete is in mass, it is advisable to use the design mix concrete.
Proportioning of Nominal Mix Concrete
(for small and scattered job and as per approval of engineer in Charge)
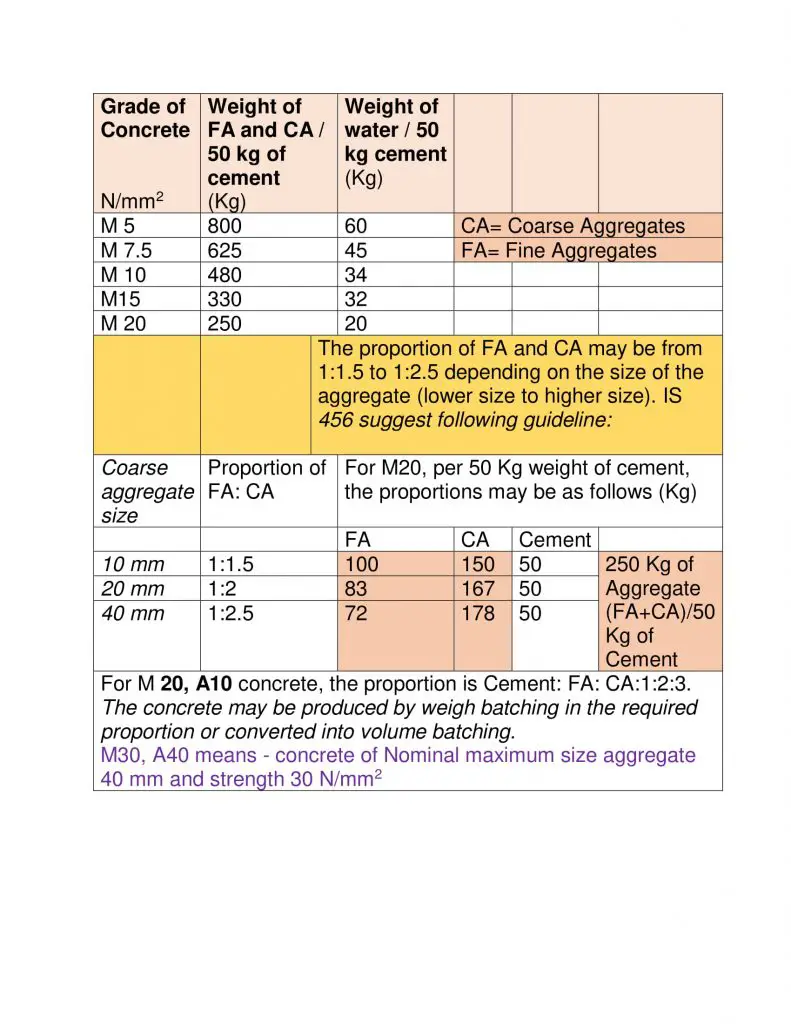
Nominal mix design may be adopted for other grades of concrete as well as discussed above…
General-Blog posts from TecConsults shall be based on the topics given in the ‘JOIN US’ page, but not limited to available list of topics on the http://techconsults.in. Viewers are now free to join TecConsults and can contact sksaxena@techconsults.in and info@techconsults.in for their suggestions for managing the main and sub topi
“We should attempt to bring nature, houses, and human beings together in a higher unity.” Ludwig

