When I started pondering on factors that boost productivity, I notices the term circadian rhythms. This gave me some more time to understand the circadian rhythms and human biological clocks, which helps us in understanding human behaviour in the workplace. This blog has included basic concepts to enhance not only productivity but also, IQ and emotional intelligence (EQ).
Topics covered
The Biological or the Body Clock
Biological Rhythm
How Biological Rhythms Work
Types of Biological Rhythms
What are Circadian Rhythms? (CR)
Reset Circadian Rhythms
The Biological or the Body Clock
Our body consists of cells.
A group of cells that have a similar structure and that function together as a unit is called a tissue.
A collection of tissues that form a functional unit specialized to perform a particular function is called an organ – such as a kidney, heart, etc.
A body made up of organs, or other parts that work together to carry on the various processes of life is called an organism.
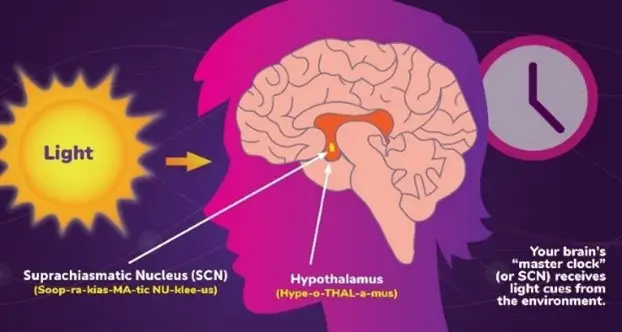
Biological clocks are organism’s natural timing devices. There are several such biological clocks, which are controlled by a master clock in the brain – SCN (suprachiasmatic nucleus).
Many physiological processes in our body are controlled by the biological clock and show circadian rhythmicity. ( Appear at regular time in the day – 24 hours)
Biological Rhythm
Biological rhythm (BR) is a phrase often used interchangeably with circadian rhythm. These rhythms are a series of bodily functions (physical processes) regulated by the body’s internal clock. They control cycles like sleep and wakefulness, body temperature, hormone secretion, and more.
How Biological Rhythms Work
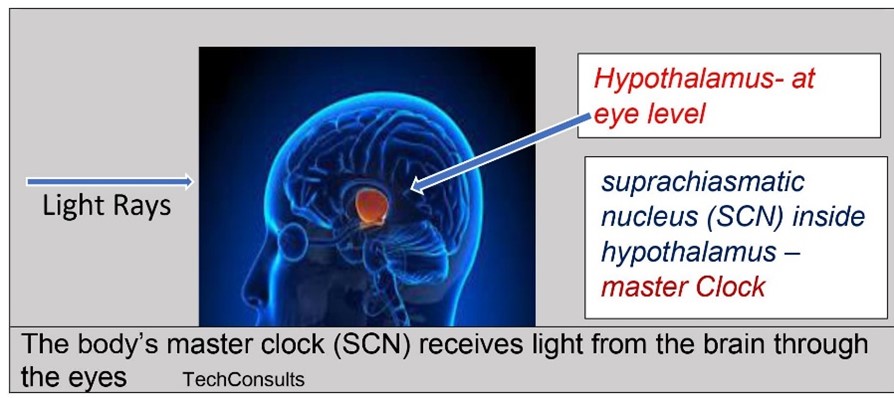
The biological rhythms are attached to the brain clock called the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN). It is in the hypothalamus.
The SCN conveys messages over the course of the day to control the body’s movement.
The hypothalamus, a structure deep in the brain, that acts as the body’s smart control / coordinating centre, is very small.
The hypothalamus responds to light and dark signals that are transmitted to the retina through the eyes. The retina sends a signal to SCN.
The SCN (The suprachiasmatic nucleus or nuclei (SCN) is a tiny region of the brain. It is responsible for controlling circadian rhythms. ) controls the production of melatonin, a hormone that inducing sleep. When there is less light, the SCN tells the brain to make more melatonin that induces sleep.
Functions of Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus has many important functions, including:
releasing hormones.
maintaining daily physiological cycles.
controlling appetite.
managing sexual behavior.
regulating emotional responses.
regulating body temperature.
More details at
https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/hypothalamus
This is the region of the cerebrum that deals with the autonomic sensory system and the pituitary organ. SCN conveys messages over the course of the day to control your body’s movement.
( The autonomic nervous system is a network of nerves throughout the body that control unconscious processes.)
The biological clocks of individual humans are different for different persons and these clocks are not the same as the normal 24-hour day clock.
And this is the reason why work and sleep patterns and behavior patterns are different for human beings. This is also valid with non-humans.
Some are early risers, some are late risers ( also categorized by the word Evening Ness, Morning Ness, Lark, Early birds, Night owls, Bear, Dolphin, Lion, Wolf, etc – also called chronotypes) because our body has been programmed to function differently at different times of the day.
Types of Biological Rhythms BR
BR name and duration are as below:
Diurnal (night and day)
Circadian (24 hours) – the 24-hour cycle that includes physiological ( relating to the branch of biology that deals with the normal functions of living organisms and their parts.) and behavioral rhythms like sleeping, waking
Ultradian (less than 24 hours) – biological rhythms with a shorter period and higher frequency than circadian rhythms
Infradian (1 month) – biological rhythms that last more than 24 hours, such as a menstrual cycle
| The circadian rhythms are body’s normal approach to keeping to its 24-hour body clock, assisting the body operate on a healthy sleep-wake plan. This plan helps in living a healthy and active lifestyle and promotes body activities in a regular way. |
What are Circadian Rhythms? (CR)
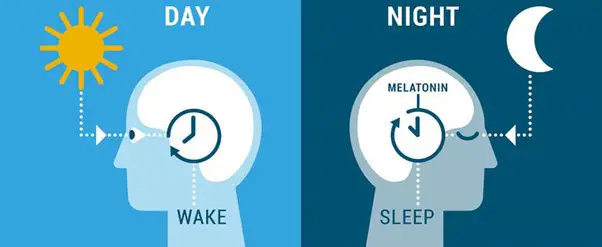
The circadian rhythm is the sleep-wake pattern of a 24-hour day for most living beings, particularly human beings. It is a part of four biological rhythms.
Biological rhythms are periodic natural changes in the body’s functions or chemicals.
Circadian rhythms are periodic bodily, mental, and behavioral changes that follow a 24-hour cycle.
The circadian clock plays a physical, mental, and behavioural role that responds to light and dark.
This clock helps regulate functions that include:
Sleep management
Food management
Health and disease management
Hormone levels
Body temperature
Work schedule management and performance
Productivity management in the workplace
Body fitness and wellness.
Helps in managing other workplace operations related to productivity.
External factors can influence biological rhythms. For instance, exposure to sunlight, drugs, and caffeine can affect sleep schedules.
The 24 – hour day cycles, control various biological processes, such as sleep and wakefulness, work activity and digestive activity and thought process etcetera. These are actions that take place in a day. The Latin words circa (“about”) and dies (“day”), are the origin of the word circadian, and thus the activities of the day are called circadian rhythms (rhythm – regular repeated pattern )
The Latin words circa (“about”) and dies (“day”), are the origin of the word circadian, and thus the activities of the day are called circadian rhythms (rhythm – regular repeated pattern )
Reset Circadian Rhythms
If the productivity is getting affected, there is need to reset your circadian rhythms for untroubled sleep and increased output. Sleep management is one of the big tasks related to productivity or output.
Resetting of circadian rhythms is gradual. Therefore, patience is needed.
Have a scheduled routine for daily actions and stick around it even on work or school holidays.
Care for fitness and wellness. The exercise done to achieve fitness and wellness produce the sleep hormone Melatonin, that helpful for sleep action. Depending on your work or school times, exercise so that you are not tired, otherwise, you may change exercise timings.
Avoid alcohol and caffeine in the evening
Reduce mobile, computer, and other screen use before sleep time as these reduce sleep-inducing hormone production. It is better to stop using these gadgets well before your scheduled sleep time.
Avoid unscheduled naps and limit the time.
It’s also ideal to be aware of your circadian rhythm because it also dictates when you’re going to be most alert during the day and when you’re going to be the most productive,” – Doctor Roth.
“People who are night owls tend to be most productive in the later evening. And people who are morning people tend to be most productive in the morning.”


