
Water is one of the most important items on the earth for sustaining life for humans and non-humans and the ongoing development activities. Life begin in oceans about 326 million years ago and then moved on to surface of the earth, and today it exists in the form of humans and non-humans.
Water has its cycle and exists in three state and is enough in quantity for requirements. However, due to increased population and development, the timely availability is not there, and it becomes scarce in lean or dry period. As such water as well as waste management has become more important in this scenario and quality aspects are discussed in this write up.

About water, Domestic and Industrial use of water, Composition of Water, Effect of development on water, Water use standards, Managing Aspects, Pollutants, pH, Water borne diseases, Water quality Indicators

“Water is the lifeblood of our bodies, our economy, our nation and our well-being. “ Stephen Johnson |
Facts about water:
Scientifically it is two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of Oxygen.
It is consumed but never used up.
It gets recycled as per hydrological cycle. The water we are using today does have the touch of our ancestors- human and non-humans.
About 65% to 70% of water exists on planet Earth.
A drop of water weighs about 0.1 gram.
Is a universal solvent. It dissolves even the rocks but takes time
Different isotopes of Hydrogen combine with oxygen to provide heavy and super heavy water
Water exists in three states: Solids, Liquids and Gases.
Temperature and Pressure are responsible for the change of state of water.
Newborn baby has around 70% water in the body. Th water contents gets reduced to around 50 % in old age.
Lack of water causes dehydration, and human being may die in about 7 days without water.
Human requirement of water is 2.0 liter per day. About 250 liter of water is required per capita per day in modern days.
Approximately 1 part of water is consumed in drinking and 99 parts are used for other purposes.
Water or Hydrological Cycle– USGS
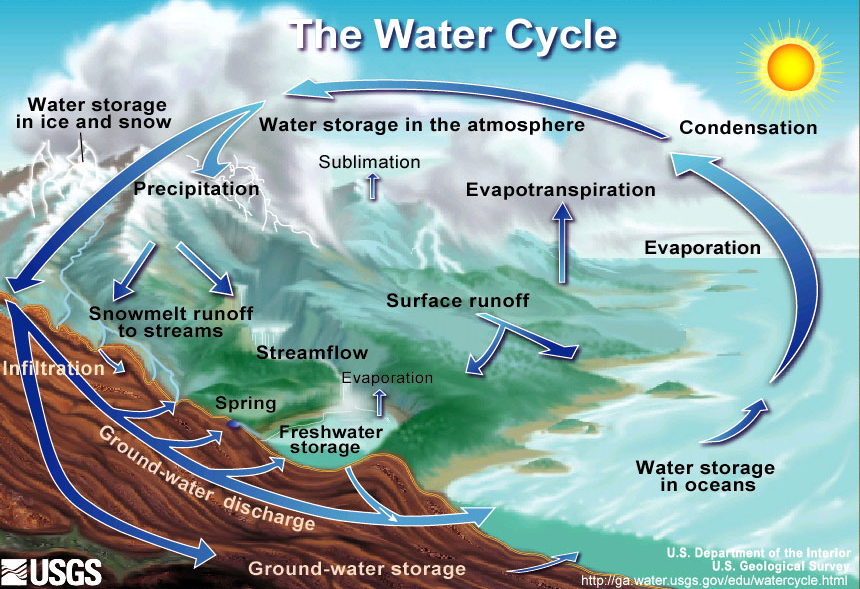
“When they went ashore the animals that took up a land life carried with them a part of the sea in their bodies, a heritage which they passed on to their children and which even today links each land animal with its origin in the ancient sea. Fish, amphibian, and reptile, warm-blooded bird and mammal – each of us carries in our veins a salty stream in which the elements sodium, potassium, and calcium are combined in almost the same proportions as in sea water. This is our inheritance from the day, untold millions of years ago, when a remote ancestor, having progressed from the one-celled stage, first developed a circulatory system in which the fluid was merely the water of the sea. In the same way, our lime-hardened skeletons are a heritage from the calcium-rich ocean of Cambrian time. Even the protoplasm that streams within each cell of our bodies has the chemical structure impressed upon all living matter when the first simple creatures were brought forth in the ancient sea. And as life itself began in the sea, so each of us begins his individual life in a miniature ocean within his mother’s womb, and in the stages of his embryonic development repeats the steps by which his race evolved, from gill-breathing inhabitants of a water world to creatures able to live on land.’
– R. Carson – The Sea Around Us (1951)
The water requirement has changed with the increase in population and now water is required for drinking, agriculture, industry, navigation etcetera in increased quantity.
This requirement of water is on daily basis and water has its own seasonal cycle of availability of water. As such the natural available water cannot fulfil the water requirements.
The gap between supply and demand are being achieved by water conservation and water management.
The requirement is to maintain proper health by consumption of water in domestic and other uses, with the use of quality- water. `
Some definitions of water in modern day environment:
White water: Water used for drinking, bathing, washing. This is the primary use of water.
Grey water: Water obtained after primary use of water is called grey water. And is used for secondary purposes such as house wash, car wash, gardening etcetera, and may also be used for toilet flushin

Dark water: The water from sinks, wash basins, and toilets is called Black water. The gray water after use is also the part of Dark Water
Water for domestic and industry use
Just like ‘quality water use’ for human consumption, the water requirement for industrial and construction use must have a good quality. The standards of quality water use exist, and the Thumb Rule of water for construction use quality is that it must be potable. Using such a rule now needs careful approach starting from construction of dwelling units for the downtrodden to middle class and high-class housing industry. The care less approach may crawl to other areas of construction as the workforce belongs to an unexperienced environment and is not aware of disadvantages of poor-quality water use in construction.
It is seen in most of the areas, that small house /office industry construction works, though are designed properly, but the construction practices are not even the fair practices.
People are mostly aware that if steel and cement are of good quality and in satisfactory quantity than they shall have the best construction.
The owners of construction units remain dependent on the skills of construction staff. Here skill development / upgradation is necessary and instead of experienced work force, the skilled workforce should be given priority in employment for better implementation of the work specifications. Repeated guidance provided on the job site make them aware of the good construction practices.
The purpose of sharing this information is that with the changes in construction environment, awareness must be created in knowing the water quality and its use in construction. And at the same time people must be aware of actions that pollutes water from construction use or domestic use of water.
Composition of Water
Composition of water, that is available from water bodies for use, depends upon, the surrounding environment (land, water, air) actions on water bodies, which also include the natural and unnatural actions, and the processes that take place in the water body environment.
These are:
Climate and weather conditions of the basin and revolves around the quantity of precipitation.
Geological conditions effect the sedimentation transportation and percolation of water. Lithology of the rocks is important.
Topography is responsible for velocity of flow effecting percolation and sedimentation transportation.
Vegetation cover -It is responsible for
Rate of flow of water to water bodies affects sedimentation process.
The quality of water added to water bodies-effluents should be treated to standards before releasing them into water bodies.
Biological conditions
Pollutants- from air, from effluents, from land
Effluents from:
Chemicals and minerals in nature
Populated areas
From Industry
From Construction sites
From water carrier system
From Sewage carrier system
From waste and water supply system
Management practices of storage water
Status of existing water
But now in thickly populated areas the water- withdrawal has lowered the water table and concentrated water is available. Surface sources cannot fulfill the requirement. They are polluted. People consume bottled water. Rivers are polluted. The condition is worse in thickly populated areas. The quality of water in hills, with less population is good and it can be used for construction and consumption with necessary precautions.
Properties of water need to be noticed /verified before using it as potable water and water for use in reinforced cement concrete construction, construction of roads, all concrete and masonry work for dams, buildings, aggregate processing, curing, offsite concrete production, precast concrete, plasters, finishing etcetera. This applies to various forms of concrete, masonry and plasters works, based on the use admixtures.
Water should be checked for the presence of required contents as the contents may be deleterious for cement and steel construction works. The frequency of water sample testing should be increased, and the test results should be verified with respect to the standards.
As per overall requirement of water, it is available in abundance and if it is used as per its availability as its cycle, there are no severe quality threats in water management. But it is not possible with the increase of population (drinking water needs) and pace of development (Construction Industry needs), To maintain the requirements in off season, water is conserved for use. The conservation of water must be based on quality aspects of management.
Effect of development on water
The sources of surface water, which were used for potable water are now getting polluted. The ground water table has gone down especially in populated areas. Water is being extracted from deep bore wells by pumping. The deep water has concentrated salts in it, and from surface use of such water in agriculture, the salts get deposited in fertile soil making it saline and less fertile.
In this changed scenario, the use of water on qualitative aspects now becomes important.
In laboratory, the strength of concrete with respect to water used is checked to assess the suitability of water regularly but at certain places particularly cities in plains, and around, the quality of water is should be checked more frequently as pH of water influences the property of water.
Some prevalent tips on quality of water |
Availability of surface water in different areas of the world is used primarily for drinking and construction and the source consists of snowmelt streams, falls and rivers. That is why the most of life exists near such sources. Civilization started along the rivers
Today water is a very important compound for everybody and with the increase of use of water, the importance of water has increased.
Water Standards
Solids | ||
Inorganic | Not > 3000 mg / liter | |
Organic | Not > 200 mg / liter | |
Suspended | Not > 2000 mg / liter | |
pH | 6.0 to 8.5 normally | (1) Find 28 days strength with source water. (2) find 28 days strength with distilled water. The strength at (1) should not be less than 10 % of the strength obtained from (2) |
Oils | If greater than 8 %, the strength gets reduced | |
Alkalis | Use 0.2 Normal H2SO4 to test on 100 ml water. If >25 ml H2SO4 is used to neutralize, the water is alkaline | |
Acids | Use 0.2 Normal NaOH to test on 100 ml water. If >5 l NaOH is used to neutralize, the water is acidin | |
Sugar | 0.5 % is OK;0.15 % will retard initial setting but 28 days strength is OK | |
Salts | ||
ZnCl2 | Retards concrete strength | |
PbNO3 | -do- | |
Na2CO3 | -do- | |
NaHCO3 | -do- | |
CaCl2 | Accelerator |
Rivers must have been the guides which conducted the footsteps of the first travelers. They are the constant lure, when they flow by our doors, to distant enterprise and adventure, and, by a natural impulse, the dwellers on their banks will at length accompany their currents to the lowlands of the globe or explore at their invitation the interior of continents.
– Henry David Thoreau
The water-needs order in priority |
Drinking |
Agriculture |
Industrial use |
Navigation |
Managing Aspects
Now with the increase of population and ongoing development, the requirement of water in most of the countries has increased
The sources of water are same but the availability of water do not remains the same throughout the year.
There is no relation between supply and demand. As such water management has become important so that it is available for use on time.
Water storage practice has come up. There is shift in trends of using water throughout the world. for example
Rainwater harvesting is picking up.
Recycled water is getting in use.
Tanks are developed for storage and use of water at community level.
Water management guidelines for domestic use and other uses are being used.
Sea water is desalinized for drinking needs along with the use of icebergs for water needs.
Water use awareness is being created.
Deep well water is mixed up with surface water for irrigation
Why this action has been taken and are being takenThe water for requirement, when not available from surface sources, it is tapped from ground water. The ground water extraction, if done in large quantity and from much deeper area of aquifer, the concentrated water comes up and when it is used particularly for irrigation, the soil becomes saline and loses its fertile power. To reduce the concentration in extracted water, surface water is added in different proportions as needed and then it is used for agriculture. It is being used in Pakistan. |
“Water is critical for sustainable development, including environmental integrity and the alleviation of poverty and hunger, and is indispensable for human health and well-being”.
United Nations
Types of Pollutants
There are two types of water pollutants from visibility point of view.
Which we can see (sediments, bed silt, suspended silt) and which we cannot see (dissolved solids, liquids and gases)
Every work site creates pollution such as from:
Excavation in soil or rock – sediments
Chemicals used in construction such as oils and Greece.
Effluent from workshops, blasting and other construction operations.
These pollutants reduce water clarity, disturbs source of food and habitat inside the water affecting the life inside.
They carry N and P nutrients which helps in algal growth.
Reduces aesthetic value of flowing and non-flowing water.
Affects the quality of water for drinking and industry use.
Suspended silt makes the water turbid which increases virus and bacteria and reduced oxygen,
Non-visual pollutants (such as acids, lime, gypsum)
These can be dissolved in water or may remain in suspension, may settle on the bed and may go deep into the water level to meet the ground water and pollute the underground reservoir.
As such the after effects of the visual and non-visual pollutants are harmful to human in non-human. The contaminated water becomes unsuitable for drinking and construction purposes.
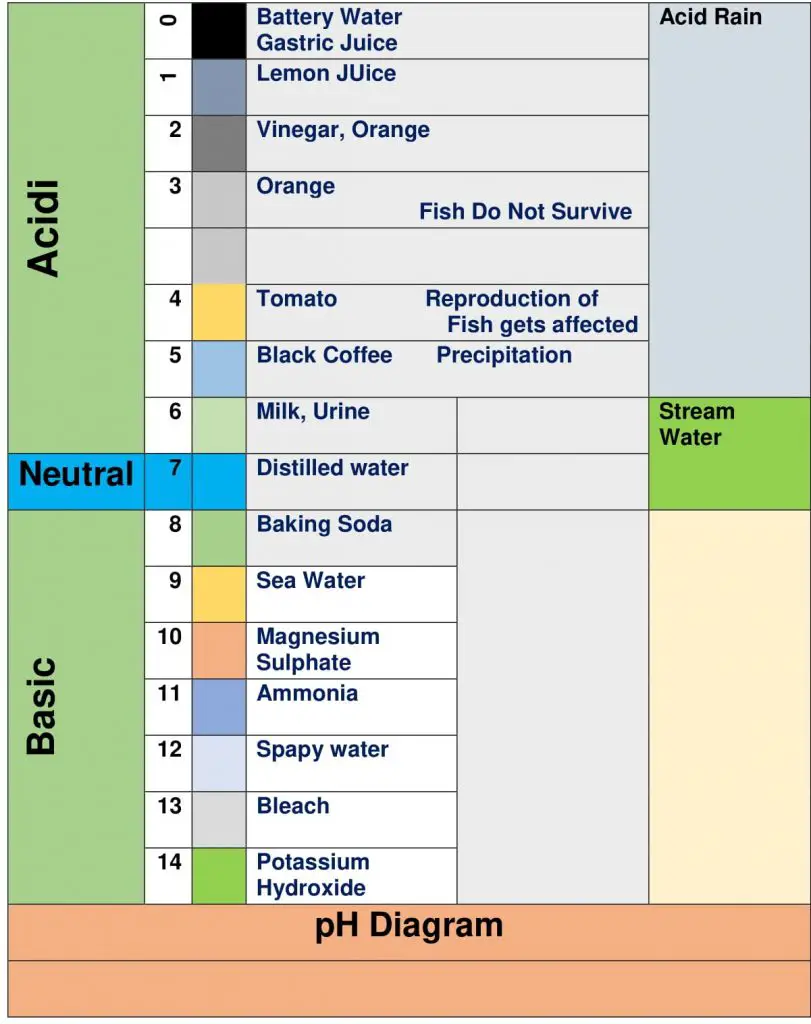
The water uses for domestic use specially for drinking may have adverse effect on the human life, if the quality of water is not good. The pH scale provides a general idea for quality of water for primary understanding. Also, readily available digital equipment proved instant quality status.
pH (potential of Hydrogen)
It is a measure of alkalinity or acidity of water at a given temperature.
Type of Solution | pH | Suitable range for surface water is 6.6 to 8’5Suitable range for drinking water is 6.0 to 8.5 | ||
Acidic | <7 | pH<6.5-water is acidic, sour in taste, water may contain Fe, Mn, Ca, Pb, Zn and is not fit for washing clothes | Hydrogen ion is more active | |
Neutral | 7 | pH of pure distilled water | Hydrogen and oxygen ion are equally active. | |
Basic or Alkaline | >7 | pH > 8.5 is hard water | OH, ion is more active |
PH diagram below shall help in understanding the Ph values and its importance in water management.
Summary of Water Quality indicators | |
Indicators | Parameters |
Radioactive | Alpha, Beta and Gamma radiation emitters |
Biological | Bacteria, Algae |
Aesthetic | Color, Odor. Organic floating matter |
Physical | Temperature, Turbidity, Dissolved solids, color, salinity, suspended solids, dissolved solids |
Chemical | · pH DO (dissolved oxygen), BOD (biological oxygen demand), Nutrients (including N & P), organic and inorganic compounds, COD |

